Types of fruit body:
There are number of fruit bodies in Ascomycota. In yeasts and related fungi the asci are not enclosed by hyphae, but in most ascomycetes they are surrounded by hyphae to form an ascocarp or ascoma. An old term for ascus is theca (Gr. theca=a case), and although this word is not now in general use, it is still found as a suffix in terms for different types of ascocarp.
Byssochlamys forms clusters of naked asci.
1. Gymnothecium
In Gymnoascus there is a loose open network of peridial hyphae forming a gymnothecium (Gr. gymnos = naked) and the asci can be seen through the network.
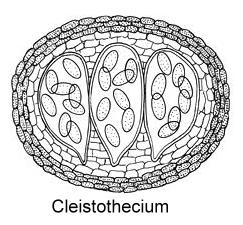
2. Cleistothecium
In most species of Aspergillus and Penicillium which
possess ascocarps, the asci are enclosed in a globose fructification with no special opening to the outside. Such ascocarps are termed cleistocarps or cleistothecia (Gr. kleistos=enclosed).
A modified cleistothecium capable of cracking open along a line of weakness is found in the Erysiphales (powdery mildews), and this is called a chasmothecium (Gr. chasma= an open mouth).
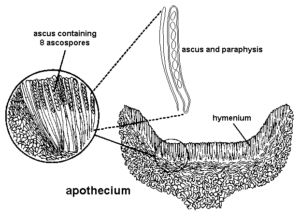 3. Apothecium
3. Apothecium
In the cup fungi (Pezizales and Helotiales) as well as in many lichenized ascomycetes the asci are borne in open saucer-shaped ascocarps, and at maturity the tips of the asci are freely exposed. Such fruit bodies are termed apothecia (Gr. apo =away from, separate).
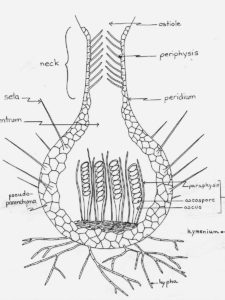
4. Perithecium
The Pyrenomycetes (e.g. Sphaeriales and Hypocreales) have perithecia (Gr. peri-= around) which are flask-shaped fruit bodies opening by a pore or ostiole.
The perithecial wall is formed from sterile cells derived from hyphae which surrounded the ascogonium during development.
Perithecia are often single, as in Sordaria and Neurospora, but in some genera they are embedded in or seated on a mass of tissue forming a perithecial stroma.
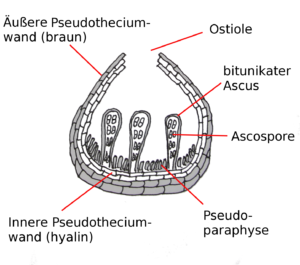
5. Pseudothecium
The development of pseudothecia differs from that of perithecia in that the asci are contained in one or several cavities (locules) formed within a pre-existing ascostroma (Gr. stroma = mattress, bed)