Following types of life histories are found in algae:
(a) Haplontic Monophasic:
- It is a primitive life cycle.
- In this case, vegetative plant body remains haploid.
- Gametes are produced by mitosis and fuse to form diploid zygote.
- First division in zygote is meiosis. It forms haploid vegetative body.
- Thus zygote is the only diploid stage in such cycles. e.g. Chlamydomonas, Ulothrix, Oedogonium, Spirogyra, Zygnema
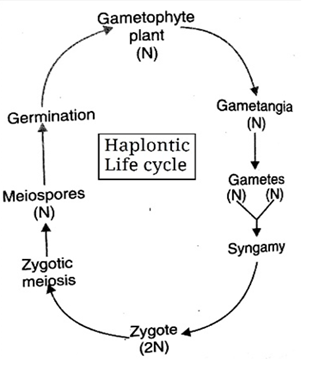
Fig: haplointic life cycle
(b) Diplontic Monophasic:
- Itis more advanced life cycle.
- In this case, vegetative stage is diploid.
- Haploid gametes are formed by meiosis.
-
- These gametes fuse to form diploid zygote.
- Zygote divides by mitosis to form vegetative body.
- Thus all life form is diploid except gametes, e.g., diatoms; Sargassum and
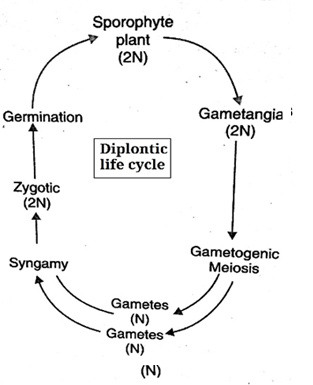
Fig: Diplontic life cycle of algae
(c) Diplohaplontic life cycle:
There are present two distinct vegetative individuals, of which one is haploid or gametophytic and other is diploid or sporophytic in nature and both alternate with each other.
- Isomorphic Diplohaplontic life cycle:
If both generations (diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte) have
similar vegetative structure, then they are called isomorphic, e.g., Ulva, Ectocarpus
- Heteromorphic Diplohaplontic:
- If plant body (sporophyte and gametophyte) has different structures,
then they are called heteromorphic.
- Gametophyte is haploid generation.
- It produces gametes by mitosis. Gametes fuse to form diploid zygote.
- Zygote form diploid sporophyte.
- Sporophyte is diploid generation. It produces spores by meiosis.
- Spores germinate to form gametophyte plant, e.g.,
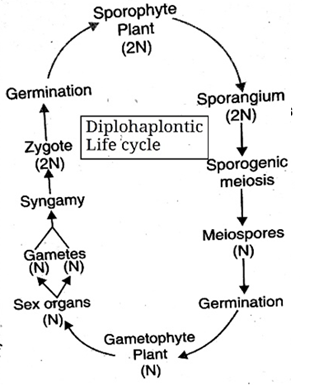
Fig: Algae, Diplohaplontic life cycle
(d) Haplobiontic Life cycle:
There are present two well-developed haploid phases in the life cycle and hence are called haplobiontic. The diploid phase is represented only by zygote.
- Plant body is gametophyte, which produces gametes
- Zygote undergoes meiosis, produces haploid nuclei and develop into haploid plant (Carposprophyte)
- Carposprophyte produces haploid carpospores.
- Carpospores germinate into heterotrichous chantransia stage.
- Erect filaments develop into gametophyte.
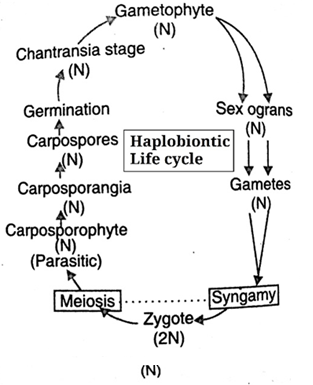
Fig: Algae haplobiontic life cycle
(e) Haplodiplobiontic or triphasic life cycle:
In this case there are present one haploid phase and two diploid phases. Because of presence of one haploid and two diploid phases, it may also name as triphasic.
- Plant body is gametophyte that produces gametes
- Zygote germinate to produce diploid carposporophyte.
- Carpospores (2n) are produced by mitosis by carposporophyte.
- Carpospores on germination produces tetrasporophyte (2n)
- Tetrasporophyte produces haploid tetraspores by meiosis.
- Tetraspores germinate to produce gametophyte.
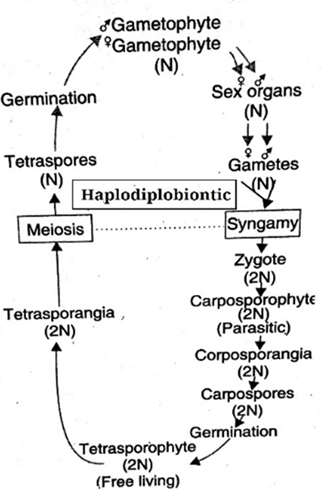
Fig: Haplodiplobiontic life cycle of algae